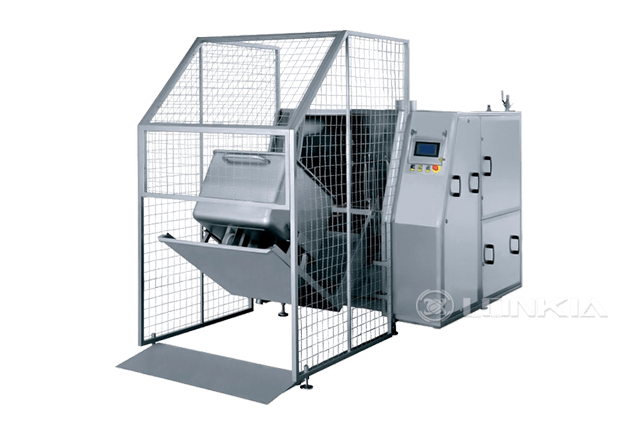
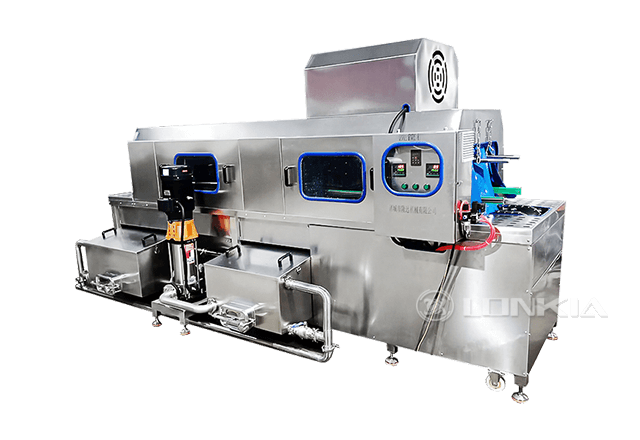
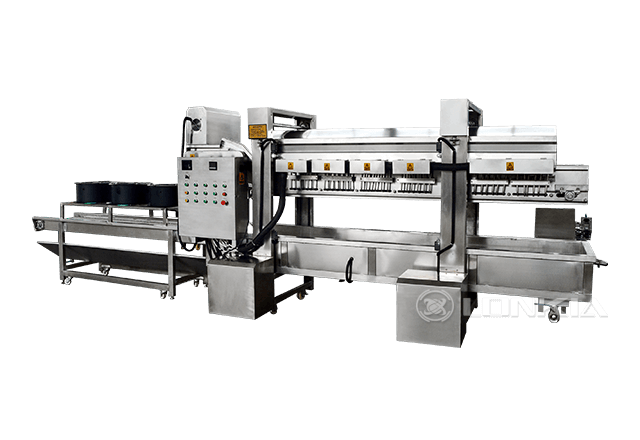
Pasteurization and ultra-pasteurization are heat treatment processes widely used in the food and beverage industry to ensure product safety and extend shelf life. While both methods aim to eliminate harmful microorganisms, they differ in temperature, duration, and the impact on the product's flavor, texture, and storage requirements. Understanding these differences is essential for choosing the right process for your business.
What Is Pasteurization?
Pasteurization is a traditional heat treatment process invented by Louis Pasteur. It involves heating food or beverages to a specific temperature for a set period, effectively killing pathogens while preserving the product's quality.
Key Features:
- Temperature and Time: Typically heated to 63°C (145°F) for 30 minutes (batch pasteurization) or 72°C (161°F) for 15 seconds (HTST - High-Temperature Short Time).
- Effect on Flavor and Nutrients: Maintains most of the product's natural flavor and nutritional value.
- Shelf Life: Extends shelf life moderately, requiring refrigeration.
Applications:
- Commonly used for milk, juices, beer, and other perishable liquids.

What Is Ultra-Pasteurization?
Ultra-pasteurization (UP) takes the process a step further, using higher temperatures for a shorter time. This method aims to achieve sterility and significantly extend shelf life.
Key Features:
- Temperature and Time: Heated to at least 138°C (280°F) for 2 seconds or less.
- Effect on Flavor and Nutrients: May slightly alter taste and reduce some nutrient levels compared to traditional pasteurization.
- Shelf Life: Produces products with an extended shelf life, even when stored at room temperature (if packaged aseptically).
Applications:
- Used for milk, cream, liquid egg products, and some juices requiring long shelf stability.
Comparison: Pasteurization vs. Ultra-Pasteurization
| Aspect | Pasteurization | Ultra-Pasteurization |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 63°C–72°C (145°F–161°F) | 138°C (280°F) or higher |
| Duration | 15 seconds to 30 minutes | 2 seconds or less |
| Shelf Life | Short to moderate (requires refrigeration) | Long (may not require refrigeration if aseptically packaged) |
| Flavor Impact | Minimal | Slight alteration |
| Nutritional Impact | Preserves most nutrients | Slight nutrient loss |
| Energy Consumption | Lower | Higher |
Which Process Is Right for Your Business?
- Choose Pasteurization If:
You prioritize maintaining the natural flavor and nutrients of your product and are distributing perishable items with moderate shelf life. - Choose Ultra-Pasteurization If:
Your focus is on maximizing shelf life and reducing refrigeration requirements, particularly for products distributed over long distances.
LONKIA: Advanced Solutions for Heat Treatment
At LONKIA, we specialize in providing cutting-edge equipment for pasteurization and ultra-pasteurization processes. Our solutions are designed to meet the needs of various industries, ensuring product safety, quality, and efficiency.
Whether you need a traditional pasteurizer for small-scale operations or an ultra-pasteurizer for high-volume production, LONKIA delivers customized equipment tailored to your business needs.
Contact Us
For expert advice and premium heat treatment equipment, contact LONKIA today. Let us help you choose the ideal solution for your food and beverage production process!